SPH related (CUDA) kernels. More...
Namespaces | |
| namespace | Launch |
| SPH related (CUDA) kernel wrappers. | |
Functions | |
| __global__ void | calculateDensity (::SPH::SPH_kernel kernel, Tree *tree, Particles *particles, int *interactions, int numParticles) |
| Calculate the density \( \rho \). More... | |
| __global__ void | internalForces (::SPH::SPH_kernel kernel, Material *materials, Tree *tree, Particles *particles, int *interactions, int numRealParticles) |
| Internal SPH forces. More... | |
| __global__ void | calculatePressure (Material *materials, Particles *particles, int numParticles) |
| Calculate the pressure. More... | |
| __global__ void | initializeSoundSpeed (Particles *particles, Material *materials, int numParticles) |
| Initialize the speed of sound \( c_s \). More... | |
| __global__ void | calculateSoundSpeed (Particles *particles, Material *materials, int numParticles) |
| Calculate the speed of sound \( c_s \). More... | |
| __global__ void | fixedRadiusNN_bruteForce (Tree *tree, Particles *particles, integer *interactions, integer numParticlesLocal, integer numParticles, integer numNodes) |
| Fixed-radius near neighbor search (brute-force method). More... | |
| __global__ void | fixedRadiusNN (Tree *tree, Particles *particles, integer *interactions, real radius, integer numParticlesLocal, integer numParticles, integer numNodes) |
| Fixed-radius near neighbor search (default method via explicit stack). More... | |
| __global__ void | fixedRadiusNN_withinBox (Tree *tree, Particles *particles, integer *interactions, integer numParticlesLocal, integer numParticles, integer numNodes) |
| Fixed-radius near neighbor search (nested stack method). More... | |
| __global__ void | fixedRadiusNN_sharedMemory (Tree *tree, Particles *particles, integer *interactions, integer numParticlesLocal, integer numParticles, integer numNodes) |
| Fixed-radius near neighbor search (brute-force method). More... | |
| __global__ void | fixedRadiusNN_variableSML (Material *materials, Tree *tree, Particles *particles, integer *interactions, integer numParticlesLocal, integer numParticles, integer numNodes) |
| Fixed-radius near neighbor search for iteratively finding appropriate smoothing length. More... | |
| __device__ void | redoNeighborSearch (Tree *tree, Particles *particles, int particleId, int *interactions, real radius, integer numParticles, integer numNodes) |
| Redo the neighbor search (FRNN). More... | |
| __global__ void | compTheta (SubDomainKeyTree *subDomainKeyTree, Tree *tree, Particles *particles, DomainList *lowestDomainList, Curve::Type curveType) |
| Find the relevant (lowest) domain list nodes as preparation for finding particles to be exchanged between processes. More... | |
| __global__ void | symbolicForce (SubDomainKeyTree *subDomainKeyTree, Tree *tree, Particles *particles, DomainList *lowestDomainList, integer *sendIndices, real searchRadius, integer n, integer m, integer relevantIndex, Curve::Type curveType) |
| Find the particles that need to be exchanged between processes to grant correctness of SPH forces. More... | |
| __global__ void | symbolicForce_test (SubDomainKeyTree *subDomainKeyTree, Tree *tree, Particles *particles, DomainList *lowestDomainList, integer *sendIndices, real searchRadius, integer n, integer m, integer relevantProc, integer relevantIndicesCounter, integer relevantIndexOld, Curve::Type curveType) |
| __global__ void | symbolicForce_test2 (SubDomainKeyTree *subDomainKeyTree, Tree *tree, Particles *particles, DomainList *domainList, integer *sendIndices, real searchRadius, integer n, integer m, integer relevantProc, integer relevantIndicesCounter, Curve::Type curveType) |
| __global__ void | collectSendIndices (Tree *tree, Particles *particles, integer *sendIndices, integer *particles2Send, integer *particlesCount, integer n, integer length, Curve::Type curveType) |
| Collect the found particles into contiguous memory in order to facilitate sending via MPI. More... | |
| __global__ void | collectSendIndices_test2 (Tree *tree, Particles *particles, integer *sendIndices, integer *particles2Send, integer *particlesCount, integer numParticlesLocal, integer numParticles, integer treeIndex, int currentProc, Curve::Type curveType) |
| __global__ void | particles2Send (SubDomainKeyTree *subDomainKeyTree, Tree *tree, Particles *particles, DomainList *domainList, DomainList *lowestDomainList, integer maxLevel, integer *toSend, integer *sendCount, integer *alreadyInserted, integer insertOffset, integer numParticlesLocal, integer numParticles, integer numNodes, real radius, Curve::Type curveType=Curve::lebesgue) |
| __global__ void | collectSendIndicesBackup (integer *toSend, integer *toSendCollected, integer count) |
| __global__ void | collectSendEntriesBackup (SubDomainKeyTree *subDomainKeyTree, real *entry, real *toSend, integer *sendIndices, integer *sendCount, integer totalSendCount, integer insertOffset) |
| __global__ void | insertReceivedParticles (SubDomainKeyTree *subDomainKeyTree, Tree *tree, Particles *particles, DomainList *domainList, DomainList *lowestDomainList, int n, int m) |
| Insert the received particles into the local tree. More... | |
| __global__ void | calculateCentersOfMass (Tree *tree, Particles *particles, integer level) |
| __global__ void | determineSearchRadii (SubDomainKeyTree *subDomainKeyTree, Tree *tree, Particles *particles, DomainList *domainList, DomainList *lowestDomainList, real *searchRadii, int n, int m, Curve::Type curveType) |
| Determine the search radius needed for SPH::Kernel::symbolicForce(). More... | |
| __global__ void | info (Tree *tree, Particles *particles, Helper *helper, integer numParticlesLocal, integer numParticles, integer numNodes) |
| Info/Debug kernel. More... | |
Detailed Description
SPH related (CUDA) kernels.
Function Documentation
◆ calculateCentersOfMass()
◆ calculateDensity()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::calculateDensity | ( | ::SPH::SPH_kernel | kernel, |
| Tree * | tree, | ||
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| int * | interactions, | ||
| int | numParticles | ||
| ) |
Calculate the density \( \rho \).
Corresponding wrapper function: SPH::Kernel::Launch::calculateDensity()
In order to compute the density, all interaction partners for each particle are iterated and those masses taken into account weighted with the smoothing kernel.
\[ The density is given by the kernel sum \begin{equation} \rho_a = \sum_{b} m_b W_{ab} \, . \end{equation} \]
- Parameters
-
kernel SPH smoothing kernel tree Tree class instance particles Particles class instance interactions interaction list/interaction partners numParticles amount of particles
Definition at line 8 of file density.cu.
◆ calculatePressure()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::calculatePressure | ( | Material * | materials, |
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| int | numParticles | ||
| ) |
Calculate the pressure.
Corresponding wrapper function: SPH::Kernel::Launch::calculatePressure()
- Parameters
-
materials Material class instance particles Particles class instance numParticles amount of particles
Definition at line 43 of file pressure.cu.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ calculateSoundSpeed()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::calculateSoundSpeed | ( | Particles * | particles, |
| Material * | materials, | ||
| int | numParticles | ||
| ) |
Calculate the speed of sound \( c_s \).
Corresponding wrapper function: SPH::Kernel::Launch::calculateSoundSpeed()
- Note
- Some materials only initialize the speed of sound and others calculate throughout the simulation.
- Parameters
-
particles Particles class instance materials Material class instance numParticles number of particles
Definition at line 35 of file soundspeed.cu.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ collectSendEntriesBackup()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::collectSendEntriesBackup | ( | SubDomainKeyTree * | subDomainKeyTree, |
| real * | entry, | ||
| real * | toSend, | ||
| integer * | sendIndices, | ||
| integer * | sendCount, | ||
| integer | totalSendCount, | ||
| integer | insertOffset | ||
| ) |
◆ collectSendIndices()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::collectSendIndices | ( | Tree * | tree, |
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| integer * | sendIndices, | ||
| integer * | particles2Send, | ||
| integer * | particlesCount, | ||
| integer | n, | ||
| integer | length, | ||
| Curve::Type | curveType | ||
| ) |
Collect the found particles into contiguous memory in order to facilitate sending via MPI.
Collect all the by SPH::Kernel::symbolicForce() previously found particles or rather indices of the particles into contiguous memory by copying to a buffer array.
- Parameters
-
[in] tree Tree class instance [in] particles Particles class instance [in] sendIndices Not contiguous particles to be sent/Array with particle indices marked to be sent [out] particles2Send Contiguous collection of indices to be sent [out] particlesCount Amount of particles to be sent [in] n Number of particles [in] length [in] curveType Space-filling curve type used (see Curve)
Definition at line 1525 of file sph.cu.
 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ collectSendIndices_test2()
◆ collectSendIndicesBackup()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::collectSendIndicesBackup | ( | integer * | toSend, |
| integer * | toSendCollected, | ||
| integer | count | ||
| ) |
◆ compTheta()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::compTheta | ( | SubDomainKeyTree * | subDomainKeyTree, |
| Tree * | tree, | ||
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| DomainList * | lowestDomainList, | ||
| Curve::Type | curveType | ||
| ) |
Find the relevant (lowest) domain list nodes as preparation for finding particles to be exchanged between processes.
This function identifies the (lowest) domain list nodes that do not belong to the corresponding process as necessary subsequent measure to find particles that need to be exchanged between processes to grant correctness of SPH forces.
- Parameters
-
[in] subDomainKeyTree SubDomainKeyTree class instance [in] tree Tree class instance [in] particles Particles class instance [in,out] lowestDomainList DomainList class instance describing the lowest domain list nodes [in] curveType Space-filling curve type used (see Curve)
Definition at line 1080 of file sph.cu.
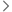 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ determineSearchRadii()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::determineSearchRadii | ( | SubDomainKeyTree * | subDomainKeyTree, |
| Tree * | tree, | ||
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| DomainList * | domainList, | ||
| DomainList * | lowestDomainList, | ||
| real * | searchRadii, | ||
| int | n, | ||
| int | m, | ||
| Curve::Type | curveType | ||
| ) |
Determine the search radius needed for SPH::Kernel::symbolicForce().
Determines the minimal distance to each domain/process that is not the domain/process of the particle itself.
- Parameters
-
[in] subDomainKeyTree SubDomainKeyTree class instance [in] tree Tree class instance [in] particles Particles class instance [in] domainList DomainList class instance [in] lowestDomainList DomainList class instance describing the lowest domain list nodes [out] searchRadii search radii/ search radius for each particle [in] n Number of particles [in] m Number of nodes [in] curveType Space-filling curve type used (see Curve)
Definition at line 2619 of file sph.cu.
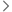 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ fixedRadiusNN()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::fixedRadiusNN | ( | Tree * | tree, |
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| integer * | interactions, | ||
| real | radius, | ||
| integer | numParticlesLocal, | ||
| integer | numParticles, | ||
| integer | numNodes | ||
| ) |
Fixed-radius near neighbor search (default method via explicit stack).
Corresponding wrapper function: SPH::Kernel::Launch::fixedRadiusNN()
Alternative methods:
- SPH::Kernel::fixedRadiusNN_bruteForce() as brute-force method
- SPH::Kernel::fixedRadiusNN_withinBox() as a (more sophisticated) tree based algorithm
Besides the straightforward brute-force approach to find the neighbors within the smoothing length as presented in SPH::Kernel::fixedRadiusNN_bruteForce(), there are two more sophisticated approaches for the FRNN search via the tree implemented. This algorithm utilizes an explicit stack for each particle to traverse the tree. In case of the node being a particle it is checked whether the distance is smaller than the smoothing length, so that this particle is added to the interaction list. In the other case of the node being a pseudo-particle, it is tested whether particles within the cell of this pseudo-particle are possibly within the range of the smoothing length and consequently either the node added to the stack or the traversal terminated for this node. This possibly early termination of traversing entire sub-trees is the key component for possible performance advantages in comparison to the brute-force approach.
- Parameters
-
[in] tree Tree class instance [in] particles Particles class instance [out] interactions interaction partners radius [in] numParticlesLocal number of local particles [in] numParticles number of particles in total [in] numNodes number of nodes
Definition at line 93 of file sph.cu.
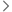 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ fixedRadiusNN_bruteForce()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::fixedRadiusNN_bruteForce | ( | Tree * | tree, |
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| integer * | interactions, | ||
| integer | numParticlesLocal, | ||
| integer | numParticles, | ||
| integer | numNodes | ||
| ) |
Fixed-radius near neighbor search (brute-force method).
Corresponding wrapper function: SPH::Kernel::Launch::fixedRadiusNN_bruteForce()
- Warning
- This implementation is primarily for comparison purposes and not for production usage!
Straight-forward brute-force method for the fixed radius near neighbor search!
Alternative methods:
- SPH::Kernel::fixedRadiusNN() as a tree based algorithm
- SPH::Kernel::fixedRadiusNN_withinBox() as a (more sophisticated) tree based algorithm
◆ fixedRadiusNN_sharedMemory()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::fixedRadiusNN_sharedMemory | ( | Tree * | tree, |
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| integer * | interactions, | ||
| integer | numParticlesLocal, | ||
| integer | numParticles, | ||
| integer | numNodes | ||
| ) |
Fixed-radius near neighbor search (brute-force method).
Corresponding wrapper function: SPH::Kernel::Launch::fixedRadiusNN_sharedMemory()
- Warning
- Experimental for now!
- Parameters
-
[in] tree Tree class instance [in] particles Particles class instance [out] interactions interaction partners [in] numParticlesLocal number of local particles [in] numParticles number of particles in total [in] numNodes number of nodes
Definition at line 592 of file sph.cu.
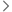 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ fixedRadiusNN_variableSML()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::fixedRadiusNN_variableSML | ( | Material * | materials, |
| Tree * | tree, | ||
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| integer * | interactions, | ||
| integer | numParticlesLocal, | ||
| integer | numParticles, | ||
| integer | numNodes | ||
| ) |
Fixed-radius near neighbor search for iteratively finding appropriate smoothing length.
Corresponding wrapper function: SPH::Kernel::Launch::fixedRadiusNN_variableSML()
This function is not for finding the near neighbor for interacting, but for finding the correct or adequate smoothing length in dependence of the desired number of interaction partners!
- Parameters
-
[in] materials Material class instance [in] tree Tree class instance [in] particles Particles class instance [out] interactions interaction partners [in] numParticlesLocal number of local particles [in] numParticles number of particles in total [in] numNodes number of nodes
Definition at line 739 of file sph.cu.
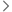 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ fixedRadiusNN_withinBox()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::fixedRadiusNN_withinBox | ( | Tree * | tree, |
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| integer * | interactions, | ||
| integer | numParticlesLocal, | ||
| integer | numParticles, | ||
| integer | numNodes | ||
| ) |
Fixed-radius near neighbor search (nested stack method).
Corresponding wrapper function: SPH::Kernel::Launch::fixedRadiusNN_withinBox()
Alternative methods:
- SPH::Kernel::fixedRadiusNN_bruteForce() as brute-force method
- SPH::Kernel::fixedRadiusNN() as a tree based algorithm
This algorithm is similar to SPH::Kernel::fixedRadiusNN(), but in addition for checking whether the cell of a pseudo-particle is possibly within the smoothing length of the particle for which the neighbors are searched for, it is checked whether the cell or box of this pseudo-particle may be in entirely within the range of the smoothing length. If this is fulfilled, all the particles beneath this pseudo-particle are added to the interaction list. This is done by a second explicit stack for which the primary explicit stack can be reused as shown
- Parameters
-
[in] tree Tree class instance [in] particles Particles class instance [out] interactions interaction partners [in] numParticlesLocal number of local particles [in] numParticles number of particles in total [in] numNodes number of nodes
Definition at line 283 of file sph.cu.
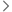 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ info()
◆ initializeSoundSpeed()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::initializeSoundSpeed | ( | Particles * | particles, |
| Material * | materials, | ||
| int | numParticles | ||
| ) |
Initialize the speed of sound \( c_s \).
Corresponding wrapper function: SPH::Kernel::Launch::initializeSoundSpeed()
- Note
- Some materials only initialize the speed of sound and others calculate throughout the simulation.
- Parameters
-
particles Particles class instance materials Material class instance numParticles number of particles
Definition at line 4 of file soundspeed.cu.
◆ insertReceivedParticles()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::insertReceivedParticles | ( | SubDomainKeyTree * | subDomainKeyTree, |
| Tree * | tree, | ||
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| DomainList * | domainList, | ||
| DomainList * | lowestDomainList, | ||
| int | n, | ||
| int | m | ||
| ) |
Insert the received particles into the local tree.
Insert the previously received particles into the local tree as similar approach to the actual tree creation in TreeNS::Kernel::buildTree().
- Parameters
-
[in] subDomainKeyTree SubdomainKeyTree class instance [in,out] tree Tree class instance [in,out] particles Particles class instance [in] domainList DomainList class instance [in] lowestDomainList DomainList class instance describing the lowest domain list nodes [in] n Number of particles [in] m Number of nodes
Definition at line 1875 of file sph.cu.
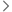 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ internalForces()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::internalForces | ( | ::SPH::SPH_kernel | kernel, |
| Material * | materials, | ||
| Tree * | tree, | ||
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| int * | interactions, | ||
| int | numRealParticles | ||
| ) |
Internal SPH forces.
Corresponding wrapper function: SPH::Kernel::Launch::internalForces()
Here, similar to the density calculation (SPH::Kernel::calculateDensity()), all the interaction partner particles are iterated for each particle and those contributions are summed.
The artificial viscosity terms can be taken into account as an additional (artificial) pressure term in the equations for conservation of momentum and energy. The additional term for each interaction pair \((a, b)\) is
\begin{align} \Pi^*_{ab} &= \begin{cases} \Pi_{ab} & \text{for } (\boldsymbol{v_a} - \boldsymbol{v_b}) \cdot (\boldsymbol{x_a} - \boldsymbol{x_b}) < 0 \\ 0 & \text{otherwise} \\ \end{cases} \\ \text{whereas} \; \,\Pi_{ab} &= \frac{-\alpha_{av} \bar{c}_{s,ab} \nu_{ab} + \beta_{av} \nu_{ab}^2}{\bar{\rho}_{ab}} \\ \text{with} \; \, \nu_{ab} &= \frac{\bar{h}_{ab}(\boldsymbol{v_a} - \boldsymbol{v_b}) \cdot (\boldsymbol{x_a} - \boldsymbol{x_b})}{(\boldsymbol{x_a} - \boldsymbol{x_b})^2+ \epsilon_{v} \bar{h}_{ab}^2} \; ,\\ \bar{\rho}_{ab} &= \frac{\rho_a + \rho_b}{2} \; \, \text{and} \\ \bar{c}_{s,ab} &= \frac{c_{s,a} + c_{s,b}}{2} \; . \end{align}
Here, \(\alpha_{av}\) and \(\beta_{av}\) determine the strength of the viscosity, \(\nu_{ab}\) is an approximation for the divergence, \(\bar{\rho}_{ab}\) is the averaged quantity for density, \(\bar{c}_{s,ab}\) for the speed of sound and \(\bar{h}_{ab}\) for the smoothing length, eventually multiplied by \(\epsilon_v\) for hardly separated particles.
- Parameters
-
kernel SPH kernel function materials Material parameters tree Tree class instance particles Particle class instance interactions interaction list/interaction partners numRealParticles amount of particles
Definition at line 4 of file internal_forces.cu.
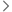 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ particles2Send()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::particles2Send | ( | SubDomainKeyTree * | subDomainKeyTree, |
| Tree * | tree, | ||
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| DomainList * | domainList, | ||
| DomainList * | lowestDomainList, | ||
| integer | maxLevel, | ||
| integer * | toSend, | ||
| integer * | sendCount, | ||
| integer * | alreadyInserted, | ||
| integer | insertOffset, | ||
| integer | numParticlesLocal, | ||
| integer | numParticles, | ||
| integer | numNodes, | ||
| real | radius, | ||
| Curve::Type | curveType = Curve::lebesgue |
||
| ) |
◆ redoNeighborSearch()
| __device__ void SPH::Kernel::redoNeighborSearch | ( | Tree * | tree, |
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| int | particleId, | ||
| int * | interactions, | ||
| real | radius, | ||
| integer | numParticles, | ||
| integer | numNodes | ||
| ) |
Redo the neighbor search (FRNN).
- Todo:
- test appropriately
- Parameters
-
[in] tree Tree class instance [in] particles Particles class instance [in] particleId particle identifier for the particle to redo the neighbor search [out] interactions interaction partners [in] radius smoothing length [in] numParticles number of particles [in] numNodes number of nodes
Definition at line 963 of file sph.cu.
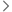 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ symbolicForce()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::symbolicForce | ( | SubDomainKeyTree * | subDomainKeyTree, |
| Tree * | tree, | ||
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| DomainList * | lowestDomainList, | ||
| integer * | sendIndices, | ||
| real | searchRadius, | ||
| integer | n, | ||
| integer | m, | ||
| integer | relevantIndex, | ||
| Curve::Type | curveType | ||
| ) |
Find the particles that need to be exchanged between processes to grant correctness of SPH forces.
Check for each particle and process that is not the corresponding process whether the particle might be needed for the SPH method since another particle on a distinct process might be within the smoothing length.
- Parameters
-
[in] subDomainKeyTree SubDomainKeyTree class instance [in] tree Tree class instance [in] particles Particles class instance [in] lowestDomainList DomainList class instance describing the lowest domain list nodes [out] sendIndices Particles or rather their indices to be sent [in] searchRadius Distance to different domain as condition for sending this particle [in] n number of particles [in] m number of nodes [in] relevantIndex (Lowest) Domain list node index to be investigated/tested [in] curveType Space-filling curve type used (see Curve)
Definition at line 1128 of file sph.cu.
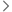 Here is the call graph for this function:
Here is the call graph for this function:◆ symbolicForce_test()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::symbolicForce_test | ( | SubDomainKeyTree * | subDomainKeyTree, |
| Tree * | tree, | ||
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| DomainList * | lowestDomainList, | ||
| integer * | sendIndices, | ||
| real | searchRadius, | ||
| integer | n, | ||
| integer | m, | ||
| integer | relevantProc, | ||
| integer | relevantIndicesCounter, | ||
| integer | relevantIndexOld, | ||
| Curve::Type | curveType | ||
| ) |
◆ symbolicForce_test2()
| __global__ void SPH::Kernel::symbolicForce_test2 | ( | SubDomainKeyTree * | subDomainKeyTree, |
| Tree * | tree, | ||
| Particles * | particles, | ||
| DomainList * | domainList, | ||
| integer * | sendIndices, | ||
| real | searchRadius, | ||
| integer | n, | ||
| integer | m, | ||
| integer | relevantProc, | ||
| integer | relevantIndicesCounter, | ||
| Curve::Type | curveType | ||
| ) |
milupHPC - SPH::Kernel Namespace Reference
Generated on Wed Aug 31 2022 12:16:54 by Doxygen 1.9.3